Dinov3: Redefining Computer Vision and Self-supervised Learning in AI
Discover how Dinov3 redefines computer vision with self-supervision, learning from 1.7 billion images without human labeling.

Discover how Dinov3 redefines computer vision with self-supervision, learning from 1.7 billion images without human labeling.
Key Points
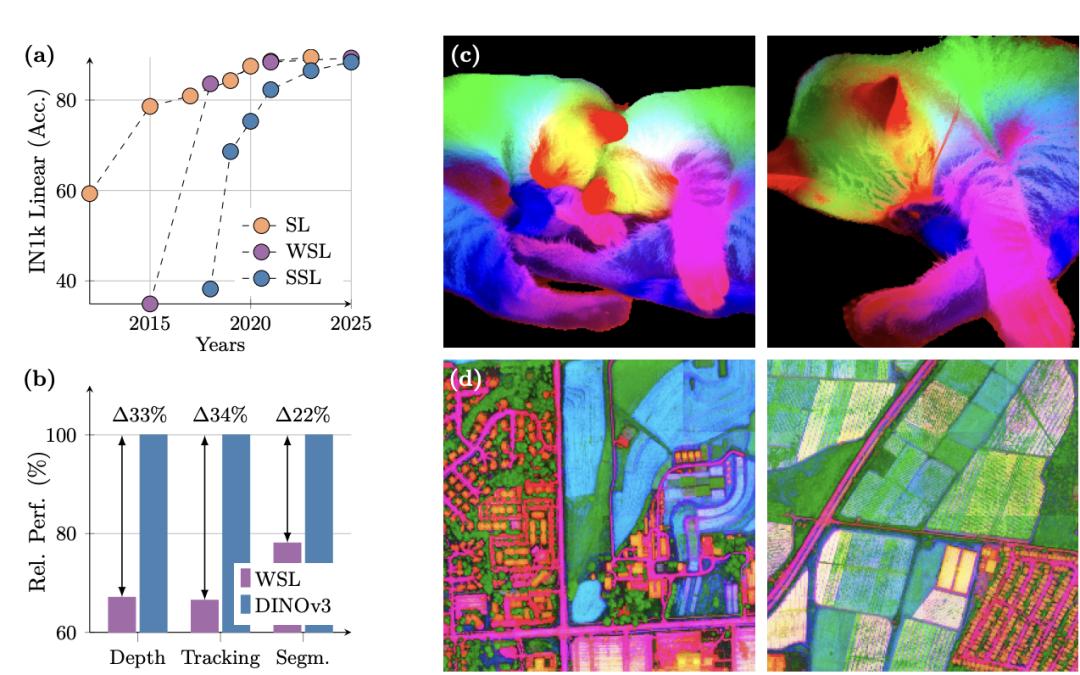
The artificial intelligence (AI) revolution is progressing strongly, and technology giants like Meta, Google, Microsoft, and ByteDance continue to push the boundaries of what is possible. Among the latest innovations, Dinov3 stands out as Meta's newest self-supervised computer vision model, marking a qualitative leap from its predecessors.
But what makes Dinov3 so special? Its strength lies in its ability to learn from an immense volume of images (1.7 billion, to be exact) without the need for human labels. In other words, Dinov3 has been trained in a self-supervised manner, allowing it to "see" and "understand" images in a much more complex and precise way than previous models.
In addition, Dinov3 is built on a universal AI backbone with 7 billion parameters, providing a robust and versatile framework that can be adapted for various applications. Its exceptional power lies in its ability to drive AI-powered robots, a field full of possibilities and promises that is now taking its first solid steps.
The term frozen universal AI backbone refers to the core architecture of the model that remains fixed during evaluation, delivering extraordinary results across a wide range of tasks without the need for retraining. In other words, once trained, Dinov3 can be applied to various scenarios without requiring fine-tuning, greatly simplifying its practical implementation.
In fact, its flexibility makes Dinov3 ideal for a wide range of applications. From autonomous robots and drones to consumer devices—and even supporting NASA in satellite image analysis and the World Resources Institute in environmental monitoring—this versatility is all thanks to Dinov3's precision and capacity.
A comparison with its predecessor, Dinov2, highlights the qualitative leap of Dinov3, not only in terms of scale but also in precision and practical application.
In contrast to the scale of Dinov3, there is Google's Gemma 3, a model developed by Google. Its strength lies in its compactness and efficiency, enabling advanced AI to run directly on mobile devices—a milestone in terms of energy consumption and privacy.
With Gemma, AI does not rely on the cloud, as it can operate locally on the device, offering clear advantages in privacy and accessibility. Its potential in fields such as medicine, law, and customer service is rooted in its ease of customization and scalability.
Microsoft is not standing still either and presents its Prompt Orchestration Markup Language (PML). PML is a structured language that simplifies interactions with AI, offering modularity, maintainability, and clarity in its use.
PML's features include a clear separation between logic and presentation, the possibility for reuse, and the incorporation of dynamic parameters. All of this is supported by integration with well-known platforms such as VS Code, NodeJS, and Python, along with an open-source policy.
ByteDance, for its part, introduces ToolTrain, a tool that streamlines error detection in large codebases, enabling fast and efficient automation of this task. Its practical relevance in the world of software development and maintenance cannot be overstated.
Although these are just a few examples, these advances clearly show how tech giants are redefining the limits of self-supervised learning in AI, gradually making tools that were once inaccessible available to non-expert users. Undoubtedly, we are living in exciting times in the world of AI. Get ready for the second part of this article, where we will explore more about the impact and opportunities these advances bring for users!
Although these advances in artificial intelligence may seem distant, they are in fact transforming our lives in practical and accessible ways. Technologies such as Dinov3, Google's Gemma 3, PML, and ToolTrain are making tools that were once exclusive to experts available to ordinary users. How is this possible?
For both users and businesses, these platforms are establishing a new standard in the artificial intelligence landscape. Here is a brief comparison:
| Model / Tool | Scale | Efficiency | Applications | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dinov3 | 7B parameters, 1.7B images | High on dense tasks | Robots, drones, satellite analysis, consumer devices | Accessible to users, label-free |
| Gemma 3 | 270M parameters | Optimized for mobile | Medicine, law, customer service | Local AI, low energy consumption |
| PML | - | Modular and maintainable | Prompt engineering and AI interaction | Widely recognized platforms |
| ToolTrain | - | Fast and precise | Code error detection | Developers |
The future looks promising. Will the broad approach of Dinov3 prevail, or the specialization and efficiency of Google's Gemma 3? Only time will tell, but one thing is clear: unprecedented opportunities are emerging for both users and businesses.
The advances made by Dinov3 and the other technologies mentioned are a testament to the unstoppable momentum of artificial intelligence. We are in an exciting moment in the history of technology, with more and more tools and opportunities available to users regardless of their level of expertise.
We invite you to continue exploring these advances, to understand how they can transform your daily life or business, and to embark on the exciting journey of discovery that is artificial intelligence. This article is just the starting point — not the end of your exploration.
What is Dinov3?
Dinov3 is a self-supervised computer vision model developed by Meta, capable of learning from 1.7 billion images without the need for human labels. It represents a significant advancement in artificial intelligence.
How does Google's Gemma 3 work?
Google's Gemma 3 AI model focuses on compactness and efficiency, enabling advanced AI to run directly on mobile devices while optimizing energy consumption and data privacy.
What is Prompt Orchestration Markup Language (PML)?
PML is a structured language developed by Microsoft that enhances interaction with AI systems, offering greater modularity, maintainability, and clarity.
How does ByteDance's ToolTrain help?
ToolTrain is a tool offered by ByteDance that quickly and accurately detects and corrects errors in large codebases. It is especially useful in software development and maintenance.
What is the AI Income Blueprint and how can I benefit from it?
The AI Income Blueprint is a program that demonstrates how anyone can generate income by leveraging the AI boom, without the need for deep technical expertise.