Artificial Intelligence Security: Risks and Strategies to Mitigate Threats
Learn how security in artificial intelligence is crucial to prevent risks and mitigate threats in the use of AI and cybersecurity.

Learn how security in artificial intelligence is crucial to prevent risks and mitigate threats in the use of AI and cybersecurity.
In today's digital age, artificial intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone of everyday and business life. From virtual assistants to advanced medical diagnostic systems and business automation with AI, its presence is pervasive. With this growing prominence, an essential concept emerges to ensure the reliability of these systems: AI security.
AI security involves protecting AI systems and ensuring that the outcomes they produce are trustworthy and ethical. It is not just about preventing technical attacks or vulnerabilities; it also means addressing a broader spectrum of risks and threats—from design errors to misuse (Source: WOMCY).
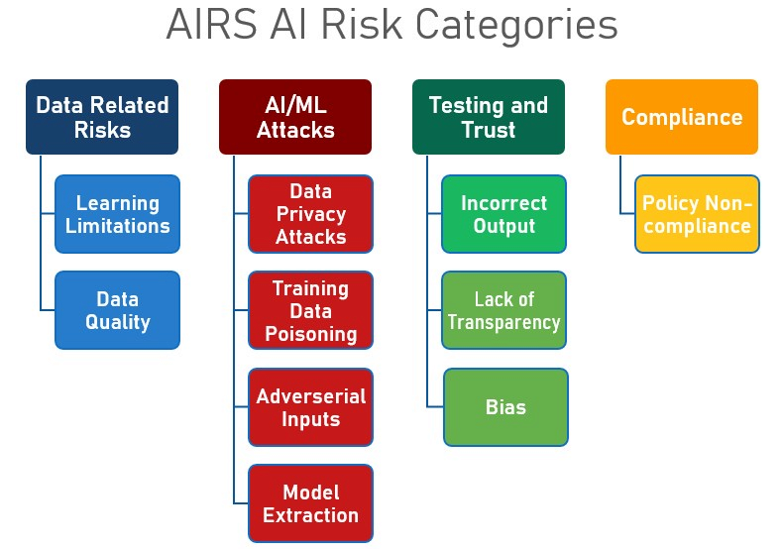
Among the main risks associated with AI, the following are worth highlighting:
In addition, specific threats in AI are both varied and sophisticated:
Furthermore, inherent vulnerabilities in AI systems include the reliance on massive volumes of data, which makes them susceptible to biases, data corruption, and supply chain attacks.
The advancement of artificial intelligence has significantly influenced both security and cybersecurity. On the one hand, AI strengthens defenses by enabling early threat detection and the automation of responses in the event of security incidents. On the other hand, it also paves the way for more sophisticated and large-scale cyberattacks, such as automated phishing and malware generation.
There are numerous examples of how AI can reinforce our defenses—like systems that detect bank fraud in real time—but also of how, in the wrong hands, it can be used to carry out targeted, hard-to-detect attacks. Particularly concerning is the impact of AI on critical infrastructure and data protection, areas where AI can represent both a strength and a risk if proper controls are not implemented.
The challenges posed by artificial intelligence are not only technical but also ethical. Here are some of the most significant ethical issues:
Additionally, data protection is crucial in AI, especially when handling personal information. It is vital to ensure data anonymization and compliance with relevant regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
A real-world example of an ethical problem is the use of deepfakes to impersonate identities in financial fraud. Controversies have also emerged around automated hiring systems that discriminate based on gender due to biased training data.
Preventing and managing AI risks is based on the application of several principles and best practices. Key measures include:
There are also concrete examples of secure AI systems developed using these principles:
Furthermore, several methodologies can help manage AI risks:
There are several key actions that developers, companies, and end users can take to improve AI security:
Regarding recommended resources and standards, the following stand out:
It is also important to stay updated on regulatory frameworks and relevant certifications:
AI security is an aspect that must be prioritized in the digital era. Proper prevention and management of risks, along with adequate data protection, are vital to ensure the reliability of AI systems. Everyone—from developers to end users—must play a part in building secure and ethical AI.
Strategically, having a clear understanding of the challenges and threats, along with adopting preventive and ethical measures, is crucial for addressing the demands of AI security. As technology advances, so do the risks. Therefore, collaboration, innovation, and business automation with AI will be key to effectively managing AI security.
AI security is the field dedicated to protecting AI systems against potential threats, vulnerabilities, and misuse, while ensuring that the outcomes produced are trustworthy and ethical.
The risks associated with AI include design errors and failures, data manipulation and misuse, and overreliance on AI systems. Specific threats include adversarial attacks, data tampering, spoofing, and deepfakes.
AI can enhance defense mechanisms by enabling early threat detection and automated responses, but it also opens the door to more sophisticated and large-scale attacks.
Ethical challenges in AI include algorithmic bias, automated decision-making, and accountability. Regarding data protection, it is critical to ensure privacy, regulatory compliance, and responsible data usage.
It is recommended to implement secure design principles from the beginning, conduct adversarial tests, and perform regular audits. Moreover, continuous threat assessment, contingency planning, and establishing technological governance are very beneficial.
Key recommendations include: conducting continuous audits and monitoring, limiting the use and sharing of personal data, and training teams on risks and best practices. It is also advisable to adopt risk management frameworks and comply with relevant regulations and certifications.